Section: Research Program
Compilation of Signal
Sequential code generation starting from a Signal specification starts with an analysis of its implicit synchronization and scheduling relations. This analysis yields the control and dataflow graphs that define the class of sequentially executable specifications and allow to generate code.
Synchronization and scheduling specifications
In Signal, the clock of a signal denotes the set of instants at which the signal is present. It is represented by a signal that is true when is present and that is absent otherwise. Clock expressions represent control. The clock (resp. ) represents the time tags at which a boolean signal is present and true (resp. false).
The empty clock is written and clock expressions combined using conjunction, disjunction and symmetric difference. Clock equations are Signal processes: the equation synchronizes the clocks and while specifies the containment of in . Explicit scheduling relations allow to schedule the calculation of signals (e.g. after at the clock ).
Synchronization and scheduling analysis
A Signal process corresponds to a system of clock and scheduling relations that denotes its timing structure. It can be defined by induction on the structure of using the inference system of Figure 5 .
x := y$ init v : ^x ^= ^y
x := y when z : ^x ^= ^y when z | y -> x when ^x
x := y default z : ^x ^= ^y default ^z | y -> x when ^y | z -> x when ^z ^- ^y
Hierarchization
The clock and scheduling relations of a process define the control flow and dataflow graphs that hold all necessary information to compile a Signal specification upon satisfaction of the property of endochrony. A process is said endochronous iff, given a set of input signals and flow-equivalent input behaviors, it has the capability to reconstruct a unique synchronous behavior up to clock-equivalence: the input and output signals are ordered in clock-equivalent ways.
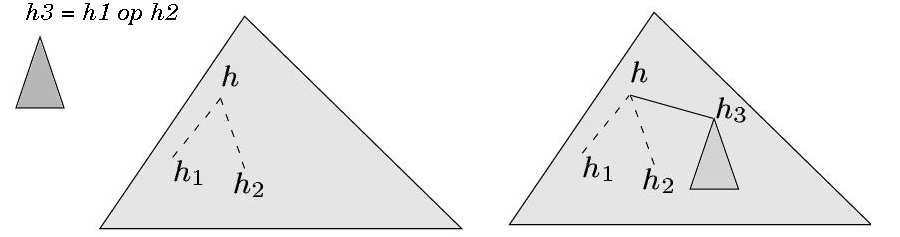
To determine the order in which signals are processed during the period of a reaction, clock relations play an essential role. The process of determining this order is called hierarchization and consists of an insertion algorithm which hooks elementary control flow graphs (in the form of if-then-else structures) one to the others. Figure 6 , right, let h3 be a clock computed using h1 and h2. Let h be the head of a tree from which h1 and h2 are computed (an if-then-else), h3 is computed after h1 and h2 and placed under h [27] .